
UC Davis - Skin Research
Objective: Determine the M-Vac™'s effectiveness at collecting DNA from male saliva applied to female skin. Traditionally, sexual assault examiners would swab a victim for biological evidence. This project investigates the alternative of using the M-Vac™ method for collecting saliva, in varying deposited quantities, from skin.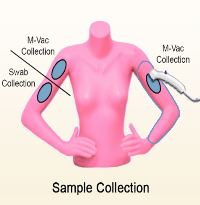 Methods: Apply male saliva in three locations on the upper arm of the female "victim," two on the right arm and one on the left. In replicates of four, repeat with 50, 25 and 5 microliters. Wait 15 minutes for the saliva to dry. M-Vac™ one saliva location on the right arm and swab the other location. M-Vac™ the entire left arm (representing an unknown location).
Methods: Apply male saliva in three locations on the upper arm of the female "victim," two on the right arm and one on the left. In replicates of four, repeat with 50, 25 and 5 microliters. Wait 15 minutes for the saliva to dry. M-Vac™ one saliva location on the right arm and swab the other location. M-Vac™ the entire left arm (representing an unknown location).
Extraction/Analysis: Extract the DNA using the QIAmp® DNA Investigator Kit (Qiagen). DNA quantification was done with Quantifiler Duo® Kit (ABI). DNA amplification was done with AmpFISTER® Identifiler® PCR Kit and YSTR Kit (ABI).
Results: The M-Vac™ collected slightly more DNA material from skin (P=0.017 at 50 microliters). The ratios of male to female DNA allowed STR amplification.
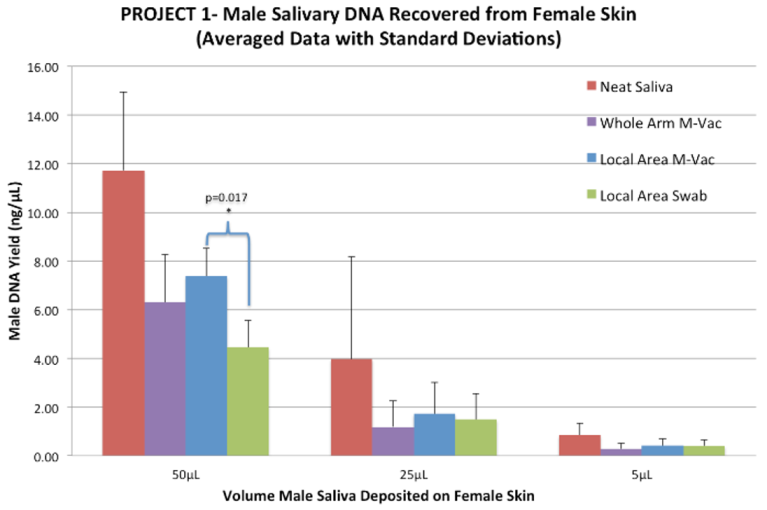
Conclusions: In sexual assaults, victims may have a hard time communicating where they were violated or where contact was made between themselves and the perpetrator. In such cases, blind swabbing is the only option, and swabbing is limited to small areas. TheM-Vac™ offers another option for collection when forensic examiners do not know where to look. In cases where the examiner knows where to sample, the M-Vac™ can be a better instrument for DNA collection on human skin. In cases where the examiner does not know where to sample and would otherwise turn to blind swabbing techniques, the M-Vac™ is a valuable alternative to retrieve foreign DNA from human skin and allows a much larger area to be sampled with the same effectiveness.
References: 2014 AAFS Poster - Comparing the M-Vac™ to Standard DNA Collection Methods for Large Surface Areas, Katie L. Caswell; Marc J. Wander; Shane E. Williams; Ruth E. Ballard, Ph.D.; Cassandra D. Calloway, Ph.D.; Christopher J. Hopkins, M.S.; William M. Green, M.D.; Sree Kanthaswamy, Ph.D.; and Edward A. Panacek, M.D.; University of California at Davis, Forensic Science Program; Sacramento State University, California Clinical Forensic Medical Training Center.